The IterationTag interface extends Tag by defining one additional
method that controls the reevaluation of its body.
A tag handler that implements IterationTag is treated as one that
implements Tag regarding the doStartTag() and doEndTag() methods.
IterationTag provides a new method:
doAfterBody().
The doAfterBody() method is invoked after every body evaluation
to control whether the body will be reevaluated or not. If doAfterBody()
returns IterationTag.EVAL_BODY_AGAIN, then the body will be reevaluated.
If doAfterBody() returns Tag.SKIP_BODY, then the body will be skipped
and doEndTag() will be evaluated instead.
Properties
There are no new properties in addition to those in Tag.
Methods
There is one new methods: doAfterBody().
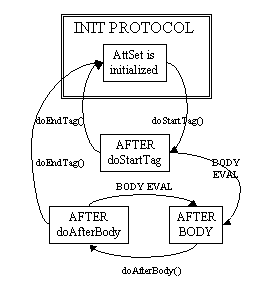
Lifecycle
Lifecycle details are described by the transition diagram
below. Exceptions that are thrown during the computation of
doStartTag(), BODY and doAfterBody() interrupt the execution
sequence and are propagated up the stack, unless the tag handler
implements the TryCatchFinally interface; see that interface for
details.
 Empty and Non-Empty Action
Empty and Non-Empty Action
If the TagLibraryDescriptor file indicates that the action must
always have an empty action, by an <body-content> entry of "empty",
then the doStartTag() method must return SKIP_BODY.
Otherwise, the doStartTag() method may return SKIP_BODY or
EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE.
If SKIP_BODY is returned the body is not evaluated, and then doEndTag()
is invoked.
If EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE is returned, the body is evaluated and
"passed through" to the current out, then doAfterBody() is invoked
and, after zero or more iterations, doEndTag() is invoked.
 Empty and Non-Empty Action
If the TagLibraryDescriptor file indicates that the action must
always have an empty action, by an <body-content> entry of "empty",
then the doStartTag() method must return SKIP_BODY.
Otherwise, the doStartTag() method may return SKIP_BODY or
EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE.
If SKIP_BODY is returned the body is not evaluated, and then doEndTag()
is invoked.
If EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE is returned, the body is evaluated and
"passed through" to the current out, then doAfterBody() is invoked
and, after zero or more iterations, doEndTag() is invoked.
Empty and Non-Empty Action
If the TagLibraryDescriptor file indicates that the action must
always have an empty action, by an <body-content> entry of "empty",
then the doStartTag() method must return SKIP_BODY.
Otherwise, the doStartTag() method may return SKIP_BODY or
EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE.
If SKIP_BODY is returned the body is not evaluated, and then doEndTag()
is invoked.
If EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE is returned, the body is evaluated and
"passed through" to the current out, then doAfterBody() is invoked
and, after zero or more iterations, doEndTag() is invoked.